NIV 858 visa priority sectors
The Government will implement a new National Innovation visa (858 visa), replacing the current Global Talent visa (subclass 858) from late 2024, to target exceptionally talented migrants who will drive growth in sectors of national importance.
This section provides examples of specialisations in each of the priority sectors for the Global Talent visa which is being replaced by the NIV visa. Specialisations listed here are not exhaustive and are representative only to provide an indication of what each sector covers for transparency.
For the purpose of prioritisation, consideration will be given as to whether the candidate’s achievements relate to specialisations articulated below in relation to the sectors. It is anticipated that novel specialisations will continue to emerge within the sectors for consideration of priority processing:
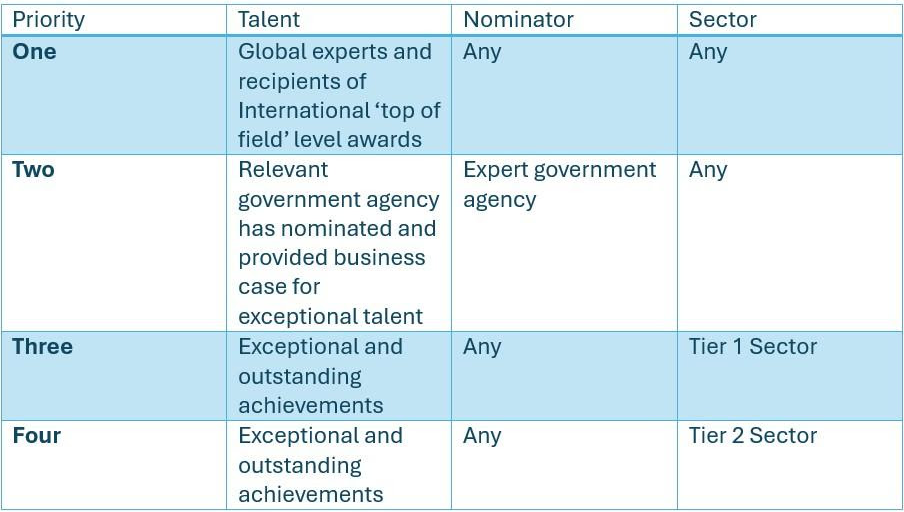
DOHA will extend invitations in the following priority order, with priority one being the highest:
| Priority one | Exceptional candidates from any sector who are global experts and recipients of international ‘top of field’ level awards. |
| Priority two | Candidates from any sector nominated on the approved Form 1000 by an expert Australian Commonwealth, State or Territory Government agency. |
| Priority three | Candidates with exceptional and outstanding achievements in a Tier One sector:
|
| Priority four | Candidates with exceptional and outstanding achievements in a Tier Two sector:
|
Invitation and visa application priority processing matrix:
Since the program commenced, more than 9000 Expressions of Interest (EOI) have been submitted, with 304 invitations issued and approximately 85 visas granted.
Priority 1 and 2 candidates are invited as soon as they are identified, while Priority 3 and 4 candidates are invited monthly.
Resources
- Advanced visualisation technologies, e.g. sensors;
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies;
- Beneficiation technologies (improving the economic value of a resource such as ore.);
- Expertise in energy saving technologies for extracting and processing ores, such as ore body mapping, geophysical tools and drilling, mineral refinement, automated trucks and robotic equipment or grinding and processing technologies; and
- Resource waste management.
Agri-food and AgTech
- Agricultural big data analytics;
- Commercialisation experience within the industry;
- Future proteins for human and animal consumption;
- Food and beverage technology;
- Individual technologies or a combination of technologies related to farm equipment, weather, seed optimisation, fertiliser and crop inputs, and irrigation;
- Precision measurement and/or application of farm inputs such as nitrogen and pesticides, gene editing, nanomaterials and synthetic biology;
- Predictive technologies around planting times, climatic forecasting and crop cycles; and
- Wearable technology, including ear-tag trackers for animal management.
Energy
- Advanced visualisation technology (e.g. sensors);
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies;
- Automation and robotics (e.g. smart sorting technologies for recycling);
- Beneficiation technologies (i.e. improving the economic value of ore);
- Recycling technology (e.g. feedstock recycling or E-waste processing);
- Traceability technologies, e.g. experience with sophisticated material trading systems that make material sources more transparent to consumers; and
- Expertise with the following fields in the sector:
- Hydrogen technology;
- Clean technologies, renewables and hybrids (including solar and wind power);
- Battery/energy storage design (specialised, grid-scale and precursors for batteries);
- Bioenergy and biofuels;
- Micro-grid design; and
- Supporting the transition to net zero carbon emissions.
Health industries
- Antimicrobial resistance;
- Biochemistry and cell biology;
- Biostatistician;
- Biotechnology;
- Biomedicine and Bioengineering;
- Cell and gene therapies – genomics;
- Clinical trials;
- Digital health;
- Health economists;
- Implantable and wearable devices (e.g. 3D printed custom devices, bionics and prosthetics);
- Infectious disease;
- Medical devices;
- Medical physicist;
- Microbiology and immunology;
- Nanotechnology and genomics;
- Neuroscience and neurology;
- Pharmaceuticals;
- Precision medicine;
- Point of care diagnostics; and
- Regenerative medicine.
Defence, Advanced Manufacturing and Space
Defence
- Augmented and virtual reality;
- Cyber Security;
- Expertise in military equipment acquisition, sustainment and evaluation;
- Robotics and automation; and
- Sensors and analytics.
Advanced manufacturing
- Advanced materials;
- Additive manufacturing (3D printing), materials resilience and repair;
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning;
- Automation & Robotics;
- Bio-manufacturing and biological integration;
- Biotechnologies;
- Digital design and rapid prototyping;
- Digitisation and automation;
- Nano-manufacturing and micro-manufacturing;
- Precision manufacturing; and
- Sustainable manufacturing and life cycle engineering.
Space
- Aviation in space
- Experience that would be of benefit to the National Civil Space Priority Areas:
- Position, navigation and timing (PNT) infrastructure (global navigation satellite systems);
- Earth observation technology and services;
- Communications technologies and services (lasers for data communication, quantum technologies for secure communication, and hybrid radio and optical communications);
- Space situational awareness and debris monitoring (including space traffic management);
- Leapfrog R&D, which includes new rocket technology, high-tech materials, space medicine, synthetic biology, quantum communications, in-orbit servicing and optical wireless communication technologies;
- Robotics and automation on Earth and in space;
- Access to space, which includes international space missions and launch activity;
- Engagement with international space and astronomy regulatory bodies.
Circular economy
- Artificial Intelligence and digital technologies;
- Bioenergy generation;
- Bio-methane production;
- Commercialisation experience within the industry;
- Development of sustainable production and supply chain practices that reduce atmospheric land and marine pollution;
- Energy infrastructure;
- Recycling and responsible manufacturing to support industries (plastics, paper, glass, tyre components, e-waste and lithium batteries);
- Reducing emissions and increasing efficient use of natural resources (including energy, water and materials);
- Waste treatment (management and reuse) and emissions technology; and
- Waste to Energy (WtE) technology (the ability to generate reliable baseload electricity that is also capable of diverting waste away from landfill and reducing carbon emissions).
Digitech
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning;
- Automation;
- Big data;
- Blockchain technology;
- Cloud computing;
- Cyber security detection, prevention and response services;
- Data and eResearch infrastructure;
- Data management and analysis;
- Data science;
- Disruptive technologies;
- Front-end development;
- Internet of Things;
- IT integrated with control systems for plant and machinery;
- Machine learning engineering;
- Network engineer/architect;
- Quantum information and computing;
- Robotics;
- Senior experience in developing and producing digital games and immersive technology;
- Smart cities;
- Smart tech;
- Software and product management/development;
- Start-ups and Entrepreneurs in the industry;
- Systems integration; and
- 3D printing.
Infrastructure and tourism
Infrastructure
Potential or ability to:
- drive economic development in regional communities;
- develop gateways to support Australia’s international competitiveness;
- improve and expand Australia’s energy infrastructure; and
- improve water security across Australia.
Tourism
Potential or ability to:
- increase the economic benefits to Australia from tourism;
- target high value travellers in the markets and tourism segments that deliver the greatest returns; and
- foster a sustainable and innovative tourism industry.
Financial services and FinTech
- Automated and predictive financial advice;
- Blockchain technology;
- Commercialisation experience within the industry;
- Digital wallets;
- Financial advice (e.g. automated and digital);
- Financial data analytics, compliance and ‘RegTech’;
- Micro-savings;
- Next generation lending, investment and wealth management;
- Online banking; and
- Platform banking and payments (e.g. contactless).
Education
- Cutting edge innovation within the Education sector
- Research and education infrastructure planning;
- Characterisation (Technologies in advanced microscopy and microanalysis that underpin modern science, medicine, engineering and industrial innovation);
- Digital Data and eResearch Platforms; and
- Platforms for Humanities, Arts and Social Sciences.
Book a meeting for a commitment free briefing with our Registered Migration Agents in Melbourne to find more about your visa options.